| CPC G06F 3/0619 (2013.01) [G06F 3/0653 (2013.01); G06F 3/0679 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
1. A memory device comprising:
a first nonvolatile memory die;
a second nonvolatile memory die stacked above the first nonvolatile memory die;
a third nonvolatile memory die;
a controller configured to control the first, second, and third nonvolatile memory dies;
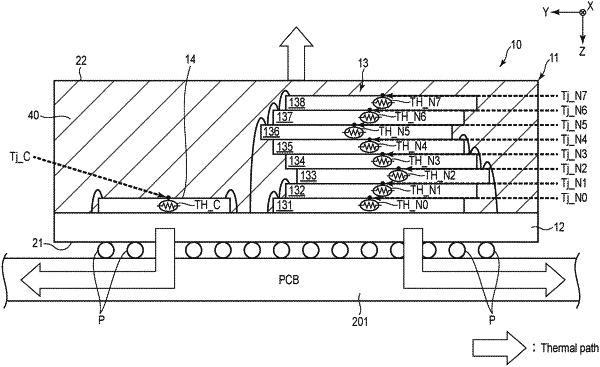
a first temperature sensor, a second temperature sensor, and a third temperature sensor incorporated respectively in the first nonvolatile memory die, the second nonvolatile memory die, and the third nonvolatile memory die;
a first surface;
a second surface located opposite to the first surface; and
a plurality of terminals exposed on the first surface, wherein
the first nonvolatile die is stacked above the third nonvolatile die,
the third nonvolatile die is closer to the first surface than the first and second nonvolatile dies,
the controller is configured to:
decide not to read a temperature measured by the third temperature sensor, or not to compare the temperature with a threshold temperature, by learning in advance temperature tendencies of the first, second, and third nonvolatile dies in a period in which access to the first, second, and third nonvolatile memory dies is in progress;
read temperatures measured by the first and second temperature sensors, from the first and second nonvolatile memory dies; and
when at least one of temperatures read from the first and second nonvolatile memory dies is equal to or higher than the threshold temperature, reduce a frequency of issue of commands to the first, second, and third nonvolatile memory dies or a speed of access to the first, second, and third nonvolatile memory dies.
|