| CPC G06F 21/577 (2013.01) [G06F 8/65 (2013.01); G06F 18/214 (2023.01); G06F 21/53 (2013.01); G06F 21/55 (2013.01); G06F 21/554 (2013.01); G06F 21/56 (2013.01); G06F 21/561 (2013.01); G06F 21/562 (2013.01); G06F 21/566 (2013.01); G06F 21/568 (2013.01); G06F 30/20 (2020.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); H04L 63/0227 (2013.01); H04L 63/0263 (2013.01); H04L 63/1416 (2013.01); H04L 63/1425 (2013.01); H04L 63/1433 (2013.01); H04L 63/1441 (2013.01); H04L 63/145 (2013.01); H04L 63/164 (2013.01); H04L 63/20 (2013.01); G06F 2221/034 (2013.01); G06F 2221/2115 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
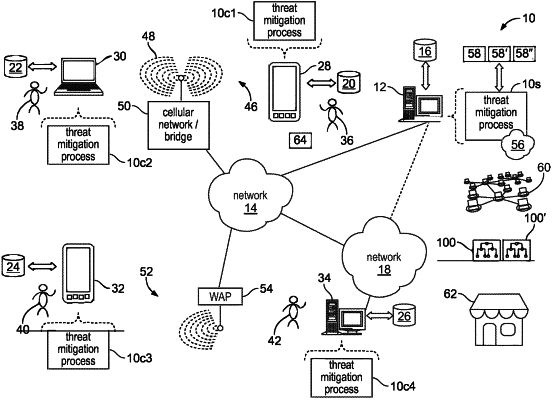
1. A computer-implemented method for threat mitigation, executed on a computing device, comprising:
obtaining first system-defined platform information concerning a first security-relevant subsystem of a plurality of security-relevant subsystems within a computing platform based upon, at least in part, monitored activity of the first security-relevant subsystem with respect to the computing platform;
obtaining at least second system-defined platform information concerning at least a second security-relevant subsystem of the plurality of security-relevant subsystems within the computing platform based upon, at least in part, monitored activity of the second security-relevant subsystem with respect to the computing platform;
combining the first system-defined platform information and the at least second system-defined platform information to form system-defined consolidated platform information, the system-defined consolidated platform information independently defining the security-relevant subsystems that are present within the computing platform;
obtaining client-defined consolidated platform information from a client information source, the client-defined consolidated platform information identifying the security-relevant subsystems that the client believes are present within the computing platform;
comparing the system-defined consolidated platform information and the client-defined consolidated platform information to define differential consolidated platform information that identifies the difference between the independently identified security-relevant subsystems and the security-relevant subsystems believed to be present by the client; and
presenting the differential consolidated platform information of the computing platform to a third-party.
|