| CPC G05D 1/0225 (2013.01) [A01D 34/008 (2013.01); B25J 11/0085 (2013.01); B25J 13/086 (2013.01); G05D 1/0259 (2013.01); G05D 1/0265 (2013.01); G05D 2201/0208 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
1. A moving robot comprising:
a body;
a motor coupled to the body and configured to provide a driving force to move the moving robot;
a sensor configured to detect respective boundary signals of a first travel area and a second travel area and a proximity boundary signal generated in a proximity boundary area which includes a portion of the first travel area and a portion of the second travel area that are positioned within a prescribed distance of each other; and
a controller configured to:
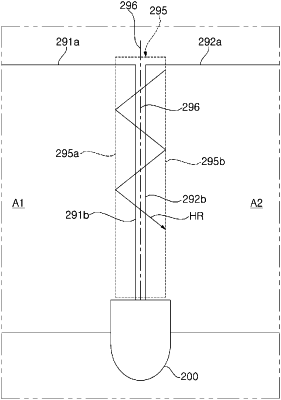
define a proximity boundary line based on the proximity boundary signal, and
manage the motor such that the moving robot performs a homing travel from a location in the first travel area to a docking station, the homing travel including a first traveling portion that includes moving from the location in the first travel area to a boundary of the first travel area and following the boundary of the first travel area based on the boundary signal of the first travel area until sensor detects the proximity boundary signal, and a second traveling portion in the proximity boundary area and based on the proximity boundary line,
wherein the controller is further configured to generate a random number that is less than a maximum threshold,
wherein the controller is further configured to manage the motor such that, during the second traveling portion of the homing travel, the moving robot travels along a homing travel route which crosses the proximity boundary line one or more times,
wherein the controller is further configured to manage the motor such that, during the second traveling portion of the homing travel, the moving robot enters the first travel area and the second travel area, alternatively,
wherein the controller is further configured to:
define a first homing boundary line and a second homing boundary line which are parallel to the proximity boundary line positioned therebetween; and
control the motor such that, during the second traveling portion of the homing travel, the moving robot changes a direction of travel at the first and second homing boundary lines to cross the proximity boundary line one or more times, and
wherein the sensor is further configured to detect a docking position signal generated in the docking station, and the controller is further configured to, when the docking position signal is detected or the moving robot crosses the proximity boundary line the random number of times during the second traveling portion of the homing travel, control the motor such that the moving robot performs a docking travel that includes moving toward the docking station.
|