| CPC G02F 1/133528 (2013.01) [C09K 19/04 (2013.01); C09K 19/0403 (2013.01); G02B 1/08 (2013.01); C09K 2019/0444 (2013.01); C09K 2323/031 (2020.08); G02B 5/3016 (2013.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
1. A polarizer which is formed of a polarizer-forming composition containing a liquid crystal compound, a first dichroic material comprising one or more molecules, and a second dichroic material comprising one or more molecules,
wherein a content of dichroic materials including the first dichroic material and the second dichroic material is in a range of 1.5 to 30 parts by mass with respect to 100 parts by mass which is a total amount of the dichroic materials and the liquid crystal compound,
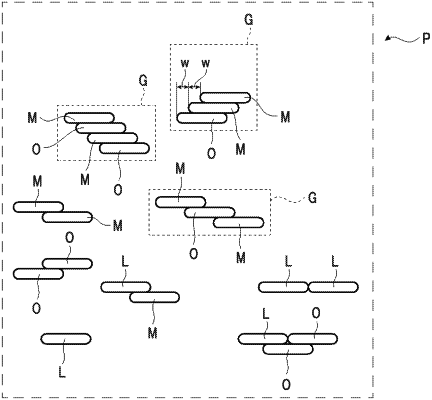
wherein the polarizer comprises an array structure formed of the first dichroic material and the second dichroic material, wherein the one or more molecules of the first dichroic material and the one or more molecules of the second dichroic material are aggregated with each other to form an aggregate of three or more dichroic molecules, and the three or more molecules of the first and second dichroic materials are periodically arranged in the aggregate,
wherein the polarizer-forming composition comprises a plurality of the aggregates,
wherein the first dichroic material is a compound represented by Formula (1),
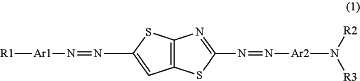 in Formula (1),
Ar1 and Ar2 each independently represent a phenylene group which may have a substituent or a naphthylene group which may have a substituent,
R1 represents a hydrogen atom, a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms which may have a substituent, an alkoxy group, an alkylthio group, an alkylsulfonyl group, an alkylcarbonyl group, an alkyloxycarbonyl group, an acyloxy group, an alkylcarbonate group, an alkylamino group, an acylamino group, an alkylcarbonylamino group, an alkoxycarbonylamino group, an alkylsulfonylamino group, an alkylsulfamoyl group, an alkylcarbamoyl group, an alkylsulfinyl group, an alkylureido group, an alkylphosphoric acid amide group, an alkylimino group, and an alkylsilyl group,
the carbon atoms of the alkyl group may be substituted with —O—, —CO—, —C(O)—O—, —O—C(O)—, —Si(CH3)2—O—Si(CH3)2—, —N(R1′)-, —N(R1′)-CO—, —CO—N(R1′)-, —N(R1′)-C(O)—O—, —O—C(O)—N(R1′)-, —N(R1′)-C(O)—N(R1′)-, —CH═CH—, —C≡C—, —C(R1′)=CH—C(O)—, or —O—C(O)—O—,
where when R1 represents a group other than a hydrogen atom, the hydrogen atom in each group may be substituted with a halogen atom, a nitro group, a cyano group, —N(R1′)2, an amino group, —C(R1′)=C(R1′)-NO2, —C(R1′)=C(R1′)—CN, or —C(R1′)=C(CN)2,
R1′ represents a hydrogen atom or a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, where when a plurality of (R1′)'s are present in each group, these may be the same as or different from one another,
R2 and R3 each independently represent a hydrogen atom, a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms which may have a substituent, an alkenyl group, an alkoxy group, an acyl group, an alkyloxycarbonyl group, an alkylamide group, an alkylsulfonyl group, an aryl group, an arylcarbonyl group, an arylsulfonyl group, an aryloxycarbonyl group, or an arylamide group,
the carbon atoms of the alkyl group may be substituted with —O—, —S—, —C(O)—, —C(O)—O—, —O—C(O)—, —C(O)—S—, —S—C(O)—, —Si(CH3)2—O—Si(CH3)2—, —NR2′-, —NR2′-CO—, —CO—NR2′-, —NR2′-C(O)—O—, —O—C—(O)—NR2′-, —NR2′-C(O)—NR2′-, —CH═CH—, —C≡C—, —C(R2′)=CH—C(O)—, or —O—C(O)—O—,
where when R2 and R3 represent a group other than a hydrogen atom, the hydrogen atom of each group may be substituted with a halogen atom, a nitro group, a cyano group, a —OH group, —N(R2′)2, an amino group, —C(R2′)=C(R2′)-NO2, —C(R2′)=C(R2′)-CN, or —C(R2′)=C(CN)2,
R2′ represents a hydrogen atom or a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, where when a plurality of (R2′)'s are present in each group, these may be the same as or different from one another,
R2 and R3 may be bonded to each other to form a ring, or R2 or R3 may be bonded to Ar2 to form a ring, and
wherein an absolute value of a difference between a maximum absorption wavelength λ2 in an absorption spectrum of a film formed of a composition that contains the second dichroic material and the liquid crystal compound but does not contain the first dichroic material, and a maximum absorption wavelength λ in a difference spectrum between an absorption spectrum of the polarizer and an absorption spectrum of the film formed of a composition that contains the first dichroic material and the liquid crystal compound but does not contain the second dichroic material is greater than 2 nm.
|