| CPC G01S 17/89 (2013.01) [G01S 17/931 (2020.01)] | 17 Claims |
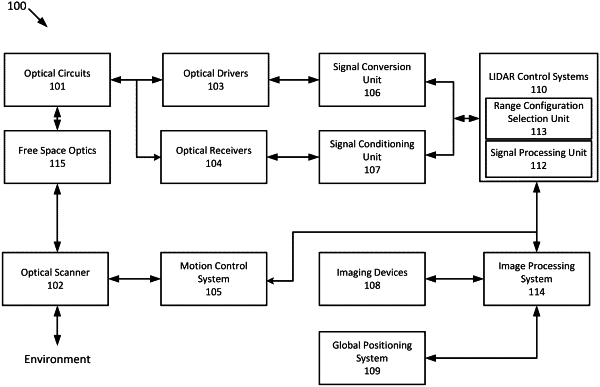
|
1. A method of generating a point cloud based on a scan pattern for a frequency-modulated continuous wave (FMCW) light detection and ranging (LIDAR) system, the method comprising:
transmitting a first optical beam towards one or more targets within a field of view (FOV), the first optical beam modulated at a first chirp rate for a first set of scan lines comprising the FOV, the first set of scan lines corresponding to a first distance of the one or more targets relative to the FMCW LIDAR system;
identifying, using a processor, one or more conditions based on the FOV to calculate a second chirp rate, wherein the identifying the one or more conditions further comprises scanning a pilot line in the scan pattern using a second optical beam modulated at the second chirp rate;
generating the scan pattern by transmitting the second optical beam towards the one or more targets within the FOV, the second optical beam modulated at the second chirp rate for a second set of scan lines comprising the FOV, the second set of scan lines corresponding to a second distance of the one or more targets relative to the FMCW LIDAR system, wherein the first distance is greater than the second distance and the first and second sets of scan lines are different; and
generating, based on the first and second optical beams, the point cloud comprising a plurality of data points related to the one or more targets, wherein a first set of data points related to a first target from the one or more targets is distinguished from a second set of data points related to a second target from the one or more targets based on the first and second chirp rates.
|