| CPC G01S 17/58 (2013.01) [G01S 7/4808 (2013.01); G01S 17/931 (2020.01); G05B 13/027 (2013.01); G06N 3/04 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A LIDAR-based method of determining an absolute speed of an object at a relatively longer distance from an ego vehicle defined as being farther from the ego vehicle than a relatively shorter distance range from the ego vehicle, the method comprising:
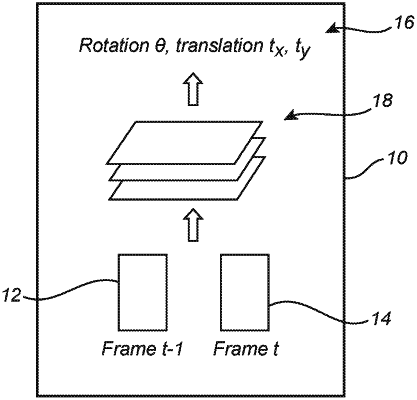
estimating a self speed of the ego vehicle using a first frame and a second frame obtained from a LIDAR sensor coupled to the ego vehicle by estimating an intervening rotation about a z axis and translations in orthogonal x and y directions over the relatively shorter distance range;
dividing each of the first frame and the second frame into multiple adjacent input ranges and estimating a relative speed of the object at the relatively longer distance by subsequently processing each frame, with each input range processed using a corresponding convolutional neural network; and
combining the estimation of the self speed with the estimation of the relative speed to obtain an estimation of the absolute speed of the object at the relatively longer distance.
|