| CPC C40B 40/10 (2013.01) [C12N 15/1037 (2013.01); C12N 15/81 (2013.01); C40B 40/08 (2013.01); C40B 50/06 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
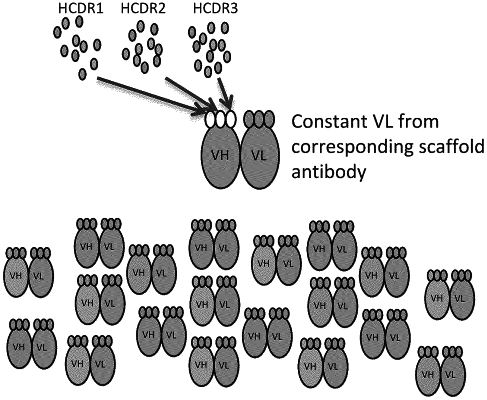
1. A method for producing a human antibody library, comprising:
deriving an antibody heavy chain from the heavy chain of a single human antibody heavy chain variable domain gene or from a single human therapeutic antibody;
providing (a) a first plurality of nucleic acids encoding a population of naturally-occurring antibody heavy chain complementary determining region 1 (CDR1) fragments, (b) a second plurality of nucleic acids encoding a population of naturally-occurring antibody heavy chain complementary determining region 2 (CDR2) fragments, and (c) a third plurality of nucleic acids encoding a population of naturally-occurring heavy chain complementary determining region 3 (CDR3) fragments;
inserting the first plurality of nucleic acids and/or the second plurality and/or the third plurality of nucleic acids into the CDR1 region and/or the CDR2 region and/or the CDR3 region, respectively, of an antibody heavy chain variable domain gene, thereby producing an antibody library;
wherein at least 90% of the population of naturally-occurring antibody heavy chain CDR1 fragments, the population of antibody heavy chain CDR2 fragments, and optionally the population of antibody heavy chain CDR3 fragments is free of members comprising one or more of:
(i) a glycosylation site,
(ii) a deamidation site,
(iii) an isomerization site,
(iv) unpaired cysteine,
(v) net charge greater than 1,
(vi) a tripeptide motif containing at least two aromatic residues,
(vii) a motif that promotes aggregation,
(viii) a poly specificity site;
(ix) a protease sensitive site,
(x) an integrin binding site,
(xi) a lysine glycation site,
(xii) a metal catalyzed fragmentation site,
(xiii) a poly specificity aggregation site; or
(xiv) a streptavidin binding motif.
|