| CPC C25D 11/26 (2013.01) [C22F 1/02 (2013.01); C22F 1/18 (2013.01); C23C 8/12 (2013.01)] | 1 Claim |
|
1. A method for increasing the interstitial oxygen as a function of depth into the surface of an article of niobium (Nb), comprising:
preparation of a surface oxide on the surface of the article of niobium;
vacuum heat treating at a constant temperature of 280 to 330° C. for 0.5 to 3 hours to dissociate the surface oxide and diffuse oxygen into the surface niobium matrix;
regrowing a surface oxide by exposing the Nb cavity to room atmosphere; and
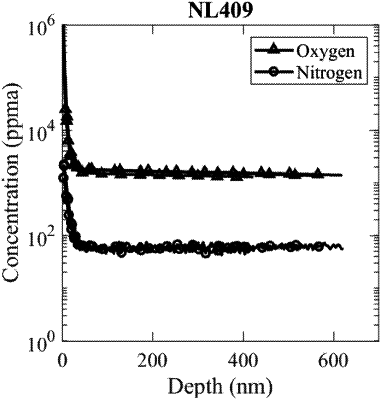
regrowing the surface oxide until a secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) depth profile verifies the O concentration of the article of niobium is at least 1000 atomic parts per million.
|