| CPC C23C 2/12 (2013.01) [C21D 9/46 (2013.01); C22C 38/02 (2013.01); C22C 38/04 (2013.01); C22C 38/06 (2013.01); C22C 38/14 (2013.01); C22C 38/32 (2013.01); C23C 2/28 (2013.01); C23C 2/40 (2013.01); C23F 15/00 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
1. A method for manufacturing a sheet metal component from a flat steel product provided with a corrosion protection coating, the method comprising:
a) providing a flat steel product produced from a steel comprising, in wt. %: 0.05-0.5% C, 0.5-3% Mn, 0.06-1.7% Si, up to 0.06% P, up to 0.01% S, up to 1.0% Al, up to 0.15% Ti, up to 0.6% Nb, up to 0.01% B, up to 1.0% Cr, up to 1.0% Mo, wherein the total of the contents of Cr and Mo is at most 1.0%, up to 0.2% Ca, up to 0.1% V, and as the remainder of iron and unavoidable impurities;
b) annealing the flat steel product in a continuous furnace having four zones A, B, C, D, which are passed through successively by the flat steel product and in which the flat steel product is annealed under an annealing atmosphere consisting in each case of 0.1-15 vol. % hydrogen and as the remainder of nitrogen as well as technically unavoidable impurities with a dew point temperature TPA, TPB, TPC, TPD at an annealing temperature GTA, GTB, GTC, GTD, the following specifications apply:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
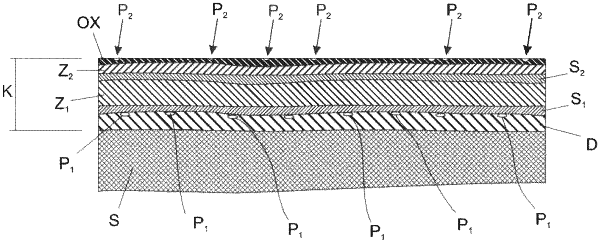
c) applying a corrosion protection coating to the flat steel product obtained in work step b), wherein the corrosion protection coating consists of, in wt. %: up to 15% Si, in total 0.1-5% of at least one alkaline earth or transition metal, up to 5% Fe in addition to the total 0.1-5% of at least one alkaline earth or transition metal, and a remainder of Al and unavoidable impurities;
d) optionally: dress rolling the flat steel product provided with the corrosion protection coating;
e) optionally: separating a board from the flat steel product;
f) heating the flat steel product or the board to a hot forming temperature which is higher than the Ac3 temperature of the steel of the flat steel product and does not exceed 1000° C. for a holding time sufficient to introduce a heat energy quantity Js of more than 100,000 kJs and at most 800,000 kJs into the flat steel product or the board;
g) hot forming the flat steel product heated to the hot forming temperature or the board heated to the hot forming temperature into the sheet metal component; and
h) cooling at least one section of the component at a cooling rate sufficient to generate a hardening structure in the at least one section of the sheet metal component.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||