| CPC B61L 23/044 (2013.01) [B61L 27/53 (2022.01); E01B 35/06 (2013.01)] | 10 Claims |
|
1. A rail breakage detection device comprising:
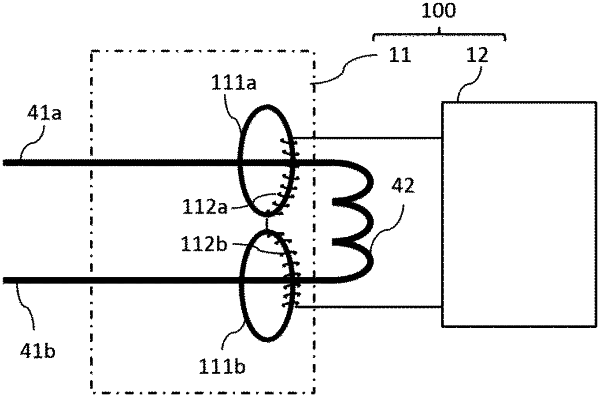
a first core part that is provided annularly along a circumferential direction of a first cable electrically connecting an electrical neutral point of an impedance bond to a prescribed block section of a first rail, the impedance bond electrically connecting the first rail and a second rail in a pair,
a second core part that is provided annularly along a circumferential direction of a second cable electrically connecting the electrical neutral point of the impedance bond to the prescribed block section of the second rail,
a first coil that is wound around the first core part to generate a first electromotive force in accordance with a current variation occurring in the first cable, and
a second coil that is connected electrically to the first coil, is wound around the second core part to generate a second electromotive force in accordance with a current variation occurring in the second cable, and generates the second electromotive force so as to cancel the first electromotive force out when the current variation occurring in the second cable is identical with the current variation occurring in the first cable in terms of a direction and a magnitude; and
a CPU configured to determine that the first rail or the second rail is broken based on an electromotive force being a sum of the first electromotive force and the second electromotive force.
|