| CPC A61M 60/804 (2021.01) [A61M 60/139 (2021.01); A61M 60/216 (2021.01); A61M 60/531 (2021.01); A61M 60/585 (2021.01); A61M 2205/3331 (2013.01); A61M 2230/65 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
1. An apparatus for a heart of a patient comprising:
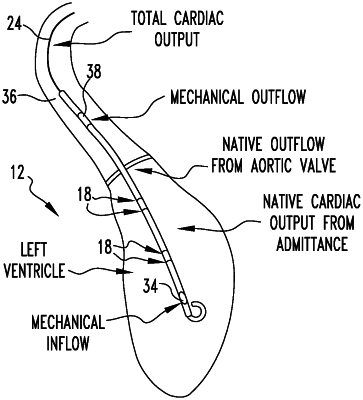
a cardiac assist device adapted to be implanted into the patient to assist the heart with pumping blood, the cardiac assist device has a shaft that is adapted to be positioned in the heart, the cardiac assist device includes a motor and an impeller disposed in the shaft which is driven by the motor to assist the heart with pumping blood, the pump draws blood from a left ventricle of the heart through an inlet port of the shaft and expels blood into an ascending aorta of the heart through an outlet port of the shaft, thereby reducing some mechanical load on the heart and promoting recovery; and
a sensor adapted to be implanted into the patient, the sensor in communication with the cardiac assist device and the heart which measures native volume of the heart using only admittance based measurements, the sensor includes electrodes directly attached to the cardiac assist device that produce signals which are used to measure the native volume of the heart, and the electrodes are in direct contact with the shaft that is positioned in the heart, the sensor includes a computer for data acquisition and analysis of the signals, the computer in communication with the electrodes, the computer produces the signals which include electrical currents to the electrodes and measures corresponding voltages to make the admittance-based measurements and analyze only the admittance-based measurements to make real-time admittance-based volume measurements of the heart.
|