| CPC A61H 3/00 (2013.01) [A61H 2003/007 (2013.01); A61H 2201/1207 (2013.01); A61H 2201/1642 (2013.01); A61H 2201/165 (2013.01); A61H 2201/5061 (2013.01); A61H 2201/5064 (2013.01); A61H 2201/5069 (2013.01); A61H 2201/5079 (2013.01); A61H 2201/5082 (2013.01); A61H 2201/5084 (2013.01); A61H 2230/605 (2013.01); A61H 2230/625 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
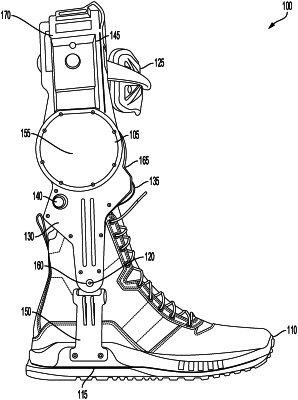
1. A method, comprising:
determining, by one or more processors coupled with memory, a metric indicative of collaboration between a user and an exoskeleton for a foot and an ankle of the user during a movement based on the combination of one or more biomechanical measurements of the user during the movement of the foot and the ankle using the exoskeleton and one or more parameters of the exoskeleton; and
controlling, by the one or more processors based on the metric, a level of a mechanical power provided by the exoskeleton to the foot and the ankle during a second movement subsequent to the movement such that the level of the mechanical power in the second movement is greater than a level of mechanical power in the movement, wherein an amount of power used by a battery of the exoskeleton during the second movement is less than an amount of power used by the battery in the movement.
|