| CPC A61B 8/0891 (2013.01) [A61B 8/06 (2013.01); A61B 8/4411 (2013.01); A61B 8/4477 (2013.01); A61B 8/4494 (2013.01); A61B 8/488 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
1. A system for measuring arterial parameters using non-imaging ultrasound, the system comprising:
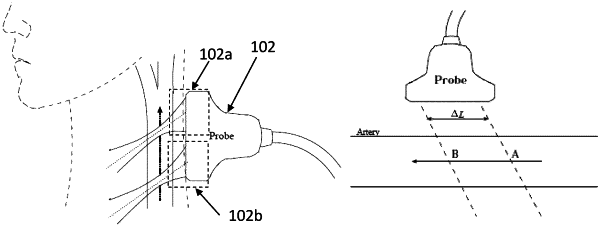
an acquisition unit for acquiring Doppler ultrasound signals from at least one blood vessel, wherein the acquisition unit comprises an ultrasound probe having a plurality of transducer elements arranged in a grid configuration, the ultrasound probe having a first non-imaging ultrasound probe and a second non-imaging ultrasound probe detachably connected to each other, wherein the ultrasound probe is configured to provide a single non-imaging ultrasound probe in an integrated configuration of the ultrasound probe, and the ultrasound probe is configured to provide two non-imaging ultrasound probes in a split configuration of the ultrasound probe, wherein the first non-imaging ultrasound probe in the split configuration is positioned to acquire a first Doppler signal and the second non-imaging ultrasound probe in the split configuration is positioned to acquire a second Doppler signal originating from a different location in a body than the first Doppler signal; and
a processing unit for processing the acquired Doppler ultrasound signals to determine a Pulse Wave Velocity (PWV) for the at least one blood vessel;
wherein the processing unit is configured to calculate a global PWV for the at least one blood vessel when the ultrasound probe is in the split configuration, and a local PWV when the ultrasound is in the integrated configuration;
wherein, when the ultrasound probe is in the split configuration, the processing unit is configured to calculate the global PWV for the at least one blood vessel based on a time delay between the first Doppler signal and the second Doppler signal; and
wherein, when the ultrasound probe is in the integrated configuration, the processing unit is configured to: determine a distension waveform indicative of (i) differences between the movements of a near wall and a far wall of the at least one blood vessel, and (ii) changes in the cross section of the at least one blood vessel, and is further configured to determine a pressure wave form based, at least partially, on the distension waveform, and determine a local PWV based using the pressure wave form.
|