| CPC A61B 5/0536 (2013.01) [A61B 5/026 (2013.01); A61B 5/316 (2021.01); A61B 5/339 (2021.01); A61B 5/7267 (2013.01); G06T 3/4007 (2013.01); G06T 11/006 (2013.01); G06T 11/60 (2013.01); G06T 17/20 (2013.01); G06T 2200/08 (2013.01); G06T 2210/24 (2013.01); G06T 2210/41 (2013.01)] | 26 Claims |
|
1. A method for non-invasively assessing presence or non-presence of significant coronary artery disease, the method comprising:
obtaining, by one or more processors, acquired data from a measurement of one or more biophysical signals of a subject, wherein the acquired data are derived from measurements acquired via noninvasive equipment configured to measure properties of a heart; and
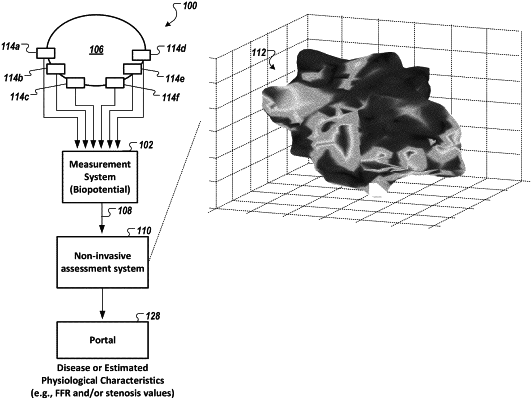
generating, by the one or more processors, a phase space model based on the acquired data, wherein the phase space model comprises a plurality of faces and a plurality of vertices, the plurality of faces and the plurality of vertices defining a volume and a surface from a triangulation operation, and wherein the plurality of vertices are defined, in part, by a residual analysis of low-energy subspace parameters generated from the acquired data;
generating, by the one or more processors, a set of tomographic images derived from the phase space model, including a first and a second tomographic image, wherein each tomographic image of the set of tomographic images is a different view of the phase space model, wherein each tomographic image of the set of tomographic images synthesizes and displays the electrical and functional characteristics of the heart, wherein the first tomographic image is generated from a projection of the phase space model in a first orientation, wherein the second tomographic image is generated from a projection of the phase space model in a second orientation that is different from the first orientation, and wherein each of the first tomographic image and the second tomographic image is generated as a grayscale tomographic image;
determining an output indicating the presence or non-presence of significant coronary artery disease, using an output of a trained neural network, wherein the trained neural network comprises a neural network trained using pixels of the grayscale first and second tomographic images that are paired with coronary angiography results assessed for the presence or non- presence of significant coronary artery disease,
wherein the output of the trained neural network is subsequently used for an assessment of presence and/or non-presence of significant coronary artery disease.
|