| CPC H01L 24/80 (2013.01) [C23C 14/083 (2013.01); C23C 14/086 (2013.01); C23C 14/10 (2013.01); C23C 14/165 (2013.01); C23C 14/35 (2013.01); C23C 14/5853 (2013.01); H01L 21/50 (2013.01); H01L 23/10 (2013.01); H01L 23/20 (2013.01); H01L 24/03 (2013.01); H01L 24/05 (2013.01); H01L 24/08 (2013.01); H01L 2224/038 (2013.01); H01L 2224/0345 (2013.01); H01L 2224/05573 (2013.01); H01L 2224/08145 (2013.01); H01L 2224/80009 (2013.01); H01L 2224/80055 (2013.01); H01L 2224/80379 (2013.01); H01L 2224/80896 (2013.01); H01L 2224/80948 (2013.01); H01L 2924/0533 (2013.01); H01L 2924/0536 (2013.01); H01L 2924/0549 (2013.01); H01L 2924/05341 (2013.01); H01L 2924/05342 (2013.01); H01L 2924/05442 (2013.01)] | 43 Claims |
|
1. A chemical bonding method comprising:
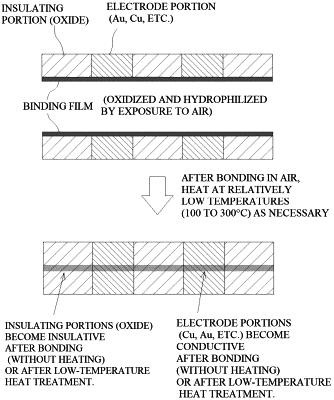
a step of forming a bonding film, which is a thin film of a metal or semiconductor formed by vacuum deposition involving rapid cooling of raw material atoms on base materials, and having many defects and hydrophilicity, and oxidized at least on its surface, on each smooth surface of two of the base materials having smooth surfaces;
a step of exposing the surfaces of the bonding films formed on the two base materials to a space having moisture to hydrophilize the surfaces of the bonding films by which moisture is adsorbed to the surface of the bonding films; and
a step of bonding the two base materials by overlaying them with each other so that the surfaces of the bonding films in a hydrophilic state contact each other.
|