| CPC G21K 1/062 (2013.01) [G01N 23/20008 (2013.01); H01S 4/00 (2013.01); H05G 2/008 (2013.01); G01N 2223/0565 (2013.01); G01N 2223/102 (2013.01); G21K 2201/061 (2013.01); G21K 2201/067 (2013.01)] | 8 Claims |
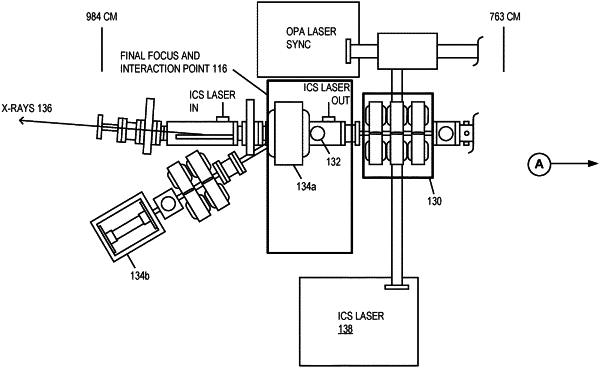
|
1. A method, comprising:
simulating diffraction in a transmission geometry of relativistic electron bunches from a crystallographic structure of a crystal, thereby simulating diffraction of the relativistic electron bunches into a plurality of Bragg peaks;
selecting, based on the simulated diffraction of the relativistic electron bunches from the crystallographic structure, a range of angles between a direction of propagation of the relativistic electron bunches and a normal direction of crystal, wherein the range of angles is selected to include an angle at which a diffraction portion into a respective Bragg peak of the plurality of Bragg peaks is maximized;
sequentially accelerating a plurality of physical electron bunches to relativistic energies, wherein the plurality of physical electron bunches are accelerated toward a physical crystal having the crystallographic structure;
diffracting the plurality of physical electron bunches off the physical crystal at different angles within the range of angles;
measuring the diffraction portion into the respective Bragg peak at the different angles within the range of angles;
selecting a final angle based on the measured diffraction portion into the respective Bragg peak at the different angles within the range of angles;
generating a pulse of light, including:
accelerating a subsequent physical electron bunch to a relativistic energy;
diffracting the subsequent physical electron bunch off the physical crystal at final angle; and
generating the pulse of light using the diffracted subsequent physical electron bunch.
|