| CPC G06F 40/284 (2020.01) [G06F 40/117 (2020.01); G06F 40/166 (2020.01); G06F 40/216 (2020.01)] | 7 Claims |
|
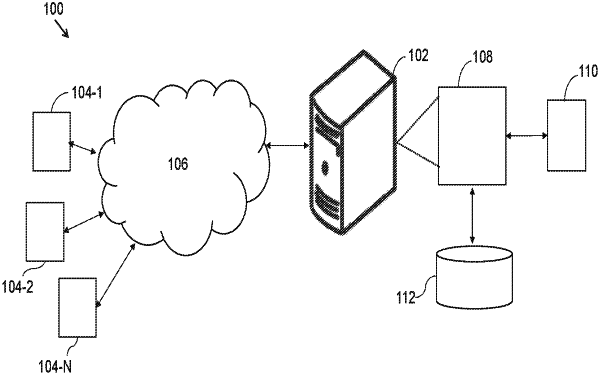
1. A processor-implemented method for statistical subject identification comprising:
receiving, via an input/output interface, a plurality of input data from a user, wherein the plurality of input data includes text strings, images, audios, and videos;
converting, via one or more hardware processors, the received images, audios, and videos into text strings using a transcription model;
pre-processing, via the one or more hardware processors, the received and converted text strings to obtain pre-processed text strings and n-grams corresponding to each of the pre-processed text strings;
computing, via the one or more hardware processors, a frequency distribution of the n-grams for the pre-processed text strings;
calculating, via the one or more hardware processors, a weightage of the n-grams for the pre-processed text strings, wherein the weightage is a frequency scaled considering size of the corresponding pre-processed text strings;
determining, via the one or more hardware processors, a ratio of sum of the calculated weightage of each n-gram across the pre-processed text strings to a maxima weightage of the n-gram;
calculating, via the one or more hardware processors, an n-gram confidence value using a box-cox transformation over the determined ratio to obtain a normal distribution of the n-gram confidence values;
identifying, via the one or more hardware processors, one or more nodes of significance from the obtained normal distribution based on one or more higher values of the calculated n-gram confidence values than a predefined dynamic threshold value, wherein the predefined dynamic threshold value depends on the obtained normal distribution;
mapping, via the one or more hardware processors, the identified one or more nodes of significance to one or more domains using a predefined domain lexicon;
converging, via the one or more hardware processors, the mapped one or more domains to a plurality of subject areas and simultaneously computing a score by adding the corresponding n-gram confidence value, associated with one or more nodes of significance, for that subject area; and
identifying, via the one or more hardware processors, at least one subject area based on the computed score to each of the one or more subjects.
|