| CPC G06F 16/24578 (2019.01) [G06N 5/041 (2013.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A system comprising:
a processor; and
memory coupled to the processor, the memory comprising computer executable instructions that, when executed by the processor, performs a method comprising:
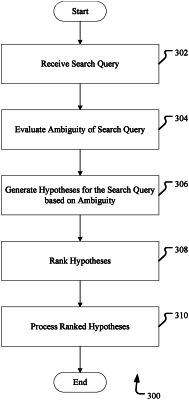
receiving a search query from a user;
identifying one or more tokens in the search query;
identifying one or more input signals associated with the one or more tokens, at least one input signal comprising an indication of an application entry point or a user access privilege;
generating a set of features using the one or more input signals;
generating one or more hypotheses based on the set of features, wherein the one or more hypotheses respectively represent a search query candidate for the search query and respectively comprise one or more of a domain, an intent, or a slot, wherein:
the domain indicates an area of knowledge or a data boundary;
the intent indicates a goal or an intention of the search query; and
the slot indicates actionable content within the search query;
ranking the one or more hypotheses based on at least the one or more input signals and a score assigned to a feature of the set of features of the one or more hypotheses, the score determined based on the least one input signal; and
processing the one or more ranked hypotheses.
|