| CPC G01N 33/493 (2013.01) [G01N 27/12 (2013.01); G01N 33/57434 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. An in vitro method to assess the risk that a subject is affected by prostate cancer, such method comprising:
a) providing a urine sample from said subject which does not comprise the last jet of a naturally voided urine sample;
b) heating the sample to above 50° C. in a closed, humidity-controlled environment;
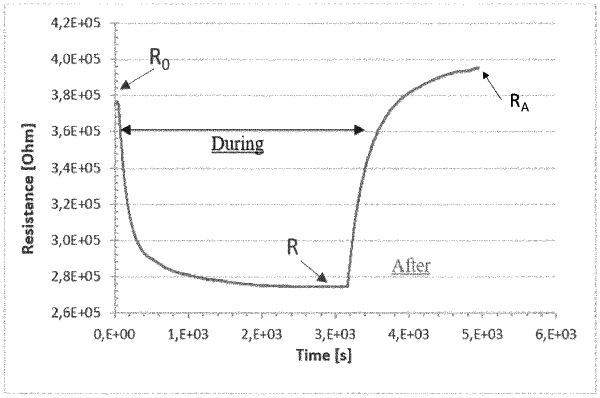
c) analysing the headspace of the sample heated in step b), under humidity control, with at least 3 Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS)-based gas sensors, wherein the metal oxide of the first gas sensor is pure or doped SnO2, the metal oxide of the second sensor is pure or doped ZnO and the metal oxides of the third sensor are pure or doped SnO2, pure or doped TiO2 and pure or doped Nb2O5;
d) comparing the values obtained in step c) to reference values for each sensor, thereby assessing the risk that a subject is affected by prostate cancer.
|