| CPC F02D 41/0255 (2013.01) [F02D 41/1454 (2013.01)] | 8 Claims |
|
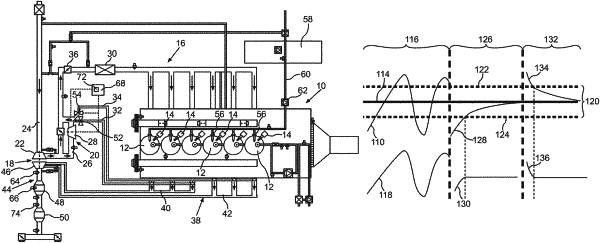
1. A method for heating a catalytic converter (48) which is disposed in an exhaust system (44) of a spark-ignition internal combustion engine (10), wherein a control unit (68) outputs a respective manipulated variable to an electrically driven additional compressor (20) and to at least one injection valve (52, 54), wherein as a result of the at least one injection valve (52, 54) being at least partially opened, air compressed by the electrically driven additional compressor (20) is introducible into the exhaust system (44) downstream of exhaust valves of the spark-ignition internal combustion engine (10) which are assigned to respective combustion chambers (12) of the spark-ignition internal combustion engine (10), and wherein signals from at least one oxygen sensor (64, 66), via which an oxygen content in exhaust gas fed to the catalytic converter (48) is detected, are supplied to a controller (72) of the control unit (68);
the method comprising the steps of:
a) switching on the electrically driven additional compressor (20);
b) at least partially opening the at least one injection valve (52, 54);
c) setting a combustion-air/fuel ratio of λ<1 in the combustion chambers (12) of the spark-ignition internal combustion engine (10);
d) detecting an actual value (128, 134) of the oxygen content in the exhaust gas by the at least one oxygen sensor (64, 66); and
e) comparing the actual value (128, 134) with a target value (114) of the oxygen content, wherein the target value corresponds to an exhaust-gas oxygen content that would be set in a region of the catalytic converter (48) if the combustion-air/fuel ratio in the combustion chambers (12) of the spark-ignition internal combustion engine (10) is approximately λ=1, wherein a manipulated variable (90, 106) output by the controller (72) on a basis of a deviation of the actual value (128, 134) from the target value (114) is kept constant when the actual value (128, 134) reaches one of two limit values (122, 124) of a value range (120) within which the target value (114) is ranged, and wherein the two limit values (122, 124) of the value range (120) deviate from the target value (114) by approximately 3%.
|