| CPC C12N 15/1065 (2013.01) [A61K 35/44 (2013.01); C12N 5/069 (2013.01); C12N 15/86 (2013.01); C12N 2506/45 (2013.01); C12N 2740/15043 (2013.01); C12N 2740/15052 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
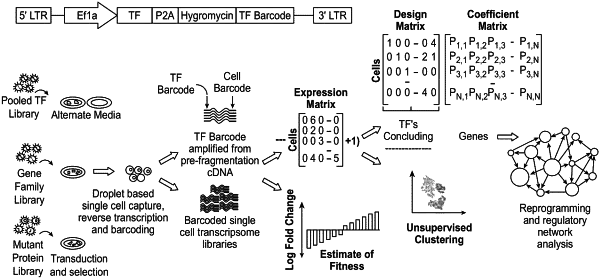
1. A method of performing a high throughput gene overexpression screen, the method comprising:
(a) transducing target cells with a barcoded open reading frame (0 RF) library of transcription factor (TF) genes comprising viral particles, wherein each of the viral particles comprises an isolated polynucleotide or vector comprising:
(i) a polynucleotide encoding an open reading frame (ORF) of a TF gene, wherein the polynucleotide is operably linked to a nucleic acid encoding a 2A peptide;
(ii) a nucleic acid encoding a selectable marker; and
(iii) a nucleic acid barcode located downstream of the selectable marker; wherein the nucleic acid barcode is located 3′ to the polynucleotide encoding the ORF of the TF gene and wherein the TF gene is a wild type TF gene, an engineered TF gene, or a mutated TF gene;
(b) performing single cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) on the transduced target cells to identify overexpressed nucleic acid barcodes;
(c) determining a fitness effect in the transduced target cells, wherein determining the fitness effect comprises determining the effect of an ORF expression on cell proliferation, viability, rate of senescence, apoptosis, DNA repair mechanism, genome stability, gene transcription, or stress response, and
(d) identifying transduced target cells comprising a significant ORF, wherein the significant ORF exhibits a cluster enrichment with a false discovery rate (FDR) of less than 10−6; and a cluster enrichment profile different from a non-TF control with a FDR less than 10−6 based on a Fisher's exact test when expressed in the target cells; and
wherein the target cells are mammalian cells selected from equine cells, bovine cells, canine cells, murine cells, porcine cells, feline cells, or human cells.
|