| CPC B25J 9/1679 (2013.01) [B25J 9/1628 (2013.01); G05B 2219/31376 (2013.01); G05B 2219/39001 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
1. A method for transferring a mass of a pourable medium (10), with which filling is to be carried out, from a first vessel (12) into a second vessel (14) by means of a robotic arm (16), wherein movement (18) of the robotic arm (16) is controlled by at least one movement parameter (BP),
comprising the following method steps:
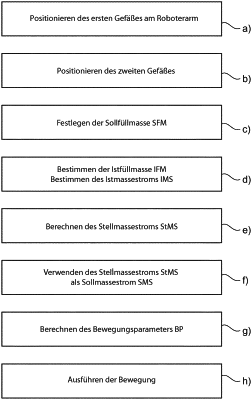
a) positioning the first vessel (12) on the robotic arm (16) such that a mass flow rate of the medium (10) from the first vessel (12) is changeable by the movement (18) of the robotic arm (16) around an axis of rotation (20),
b) positioning the second vessel (14) such that medium (10) poured out of the first vessel (12) gets into the second vessel (14) essentially by the effect of gravity,
c) defining the mass of the medium (10) that is to be filled into the second vessel (14) as the target filling mass (SFM),
d) determining the mass of the medium (10) that has been filled into the second vessel (14) as the actual filling mass (IFM), and also the change in the actual filling mass (IFM) of the medium (10) into the second vessel (14) over time as the actual mass flow rate (IMS),
e) calculating a manipulated mass flow rate (StMS) as a manipulated variable (26) of a first control loop (28), taking into account the actual filling mass (IFM) and the target filling mass (SFM),
f) using the manipulated variable (26) of the first control loop (28) as a reference variable (30) of a second control loop (32) to the effect that the calculated manipulated mass flow rate (StMS) is used as the target mass flow rate (SMS),
g) calculating the at least one movement parameter (BP) of the robotic arm (16) as a manipulated variable (40) of the second control loop (32), taking into account the target mass flow rate (SMS) and the actual mass flow rate (IMS), wherein the at least one movement parameter characterizes the rotating movement around an axis, and
h) executing the movement (18) of the robotic arm (16) on the basis of the at least one movement parameter (BP).
|