| CPC A61B 5/6844 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0075 (2013.01); A61B 5/01 (2013.01); A61B 5/0531 (2013.01); A61B 5/1114 (2013.01); A61B 5/442 (2013.01); A61B 5/7221 (2013.01); A61B 5/746 (2013.01); A61B 2560/0209 (2013.01); A61B 2560/0223 (2013.01); A61B 2562/0219 (2013.01); A61B 2562/0261 (2013.01); A61B 2562/0271 (2013.01)] | 21 Claims |
|
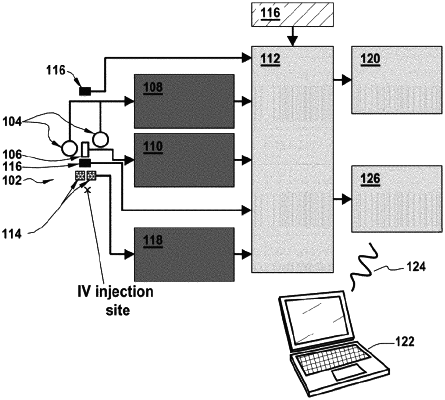
1. A sensor system for automated detection of intravenous (IV) infiltration, the sensor system comprising:
a processing device comprising at least one processor and memory, wherein the processing device is configured to be physically separated from a subject such that the subject is untethered from the processing device;
a first sensor having wireless communication capability to communicate with the processing device, the first sensor comprising one of a physiological state sensor or a movement sensor; and
an electrical bioimpedance (EBI) sensor having wireless communication capability to communicate with the processing device,
wherein the memory of the processing device has instructions stored thereon that, when executed by the processor, cause the processing device to:
obtain readings from the EBI sensor and the first sensor;
determine whether the readings from the EBI sensor are questionable using the readings from the first sensor obtained in a time frame relative to the readings from the EBI sensor; and
detect IV infiltration based on the readings from the EBI sensor if the readings from the EBI sensor are determined not to be questionable, wherein IV infiltration is detected if the readings of the EBI sensor are within a first predetermined range.
|