| CPC H02P 5/50 (2013.01) [H02P 21/0017 (2013.01); H02P 21/22 (2016.02)] | 8 Claims |
|
1. A method for model predictive current control for a two-motor torque synchronization system, wherein the method is suitable for a two-motor torque synchronization system driven by an indirect matrix converter and comprises:
1) Generating a PWM control signal through a rectifier stage controller by a rectifier stage of the indirect matrix converter adopting a space vector modulation strategy without zero vector, and providing a stable and reliable DC output voltage for an inverter stage of the indirect matrix converter subsequently,
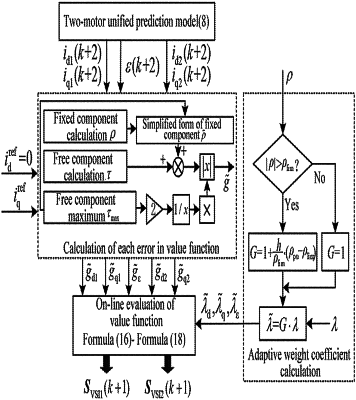
2) Establishing a two-motor unified prediction model by taking the two-motor torque synchronization system driven by two coaxially and rigidly connected motors with a same load as a subject, torque synchronization performance and current tracking performance between the motors as main control objectives, and a current value of each motor and a torque synchronization error ϵ between the motors as a state variable,
3) Inputting the state variable and an input voltage of a previous moment, obtaining a predicted value of the state variable at a next moment as an output through the two-motor unified prediction model, analyzing a composition of each error item in a weighted sum value function in a value function evaluation unit for model predictive current control, normalizing each error value by focusing on an offset degree of a free component of each error to a fixed component, and proposing a value function based on the free component of the error item, and
4) Proposing an adaptive weight coefficient without artificial iterative comparison and applying the adaptive weight coefficient to a model prediction current control of the two-motor torque synchronization system for selecting the weight coefficient in the value function based on the free component of the error item; adjusting the weight coefficient online and in real time by an adaptive factor according to a running state of the system, and meeting requirements of various working conditions with expected torque synchronization performance and current tracking performance of the system into account.
|