| CPC G11C 11/5607 (2013.01) [G11C 11/161 (2013.01); G11C 11/1657 (2013.01); G11C 11/1659 (2013.01); G11C 11/1673 (2013.01); G11C 11/1675 (2013.01); H01L 24/08 (2013.01); H01L 25/0657 (2013.01); H10B 61/10 (2023.02); H10N 50/80 (2023.02); H10N 50/85 (2023.02); H01L 2224/08145 (2013.01); H01L 2225/06506 (2013.01); H01L 2225/06541 (2013.01); H01L 2225/06562 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
17. A memory system, comprising:
a cross-point array comprising a plurality of word lines, a plurality of bit lines, and a plurality of magnetoresistive random access memory (MRAM) cells, wherein each MRAM cell resides between a cross-point of one of the plurality of word lines and a corresponding one of the plurality of bit lines, wherein each MRAM cell comprises a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) in series with a threshold switching selector; and
a control circuit in communication with the cross-point array, wherein the control circuit is configured to:
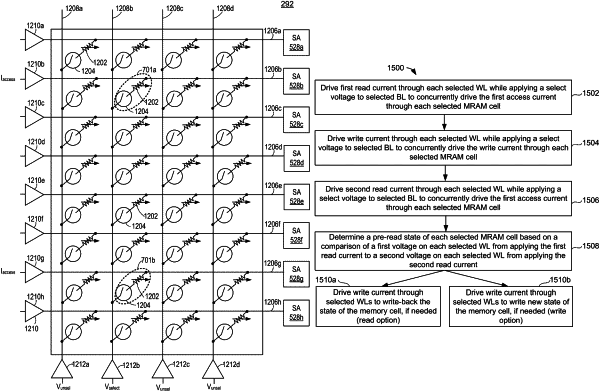
drive first fixed magnitude read currents concurrently and separately through each of a plurality of selected MRAM cells;
drive fixed magnitude write currents concurrently and separately through each of the plurality of selected MRAM cells after driving the first fixed magnitude read currents separately through each of the plurality of selected MRAM cells;
drive second fixed magnitude read currents concurrently and separately through each of the plurality of selected MRAM cells after driving the fixed magnitude write currents separately through each of the plurality of selected MRAM cells; and
determine a state of each of the selected MRAM cells based on a comparison of respective first voltages across each respective selected MRAM cell in response to the first fixed magnitude read currents and respective second voltages across each respective selected MRAM cell in response to the second fixed magnitude read currents.
|