| CPC G06T 7/0014 (2013.01) [A61B 6/12 (2013.01); A61B 6/487 (2013.01); A61B 6/5235 (2013.01); A61B 34/10 (2016.02); A61B 34/20 (2016.02); G06T 11/003 (2013.01); A61B 6/5247 (2013.01); A61B 2034/105 (2016.02); A61B 2034/2046 (2016.02); A61B 2034/2061 (2016.02); A61B 2034/2065 (2016.02); A61B 2090/3762 (2016.02); G06T 2207/10064 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10072 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30004 (2013.01)] | 30 Claims |
|
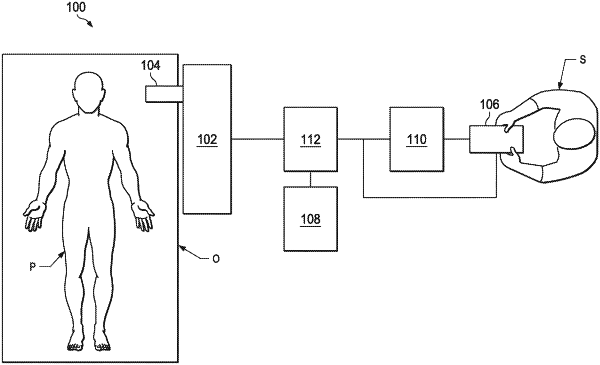
1. A robotic medical system comprising:
a flexible tubular instrument with a distal portion;
a display system; and
one or more computer readable media with instructions for:
controlling movement of the distal portion as the instrument is advanced toward an anatomical target in a patient's anatomy;
receiving a set of intraoperative images of at least the anatomical target;
reconstructing the anatomical target in three dimensions based at least in part on the set of intraoperative images; and
displaying in real time, on the display system, an additional intraoperative image of a portion of the patient's anatomy and an overlay on the additional intraoperative image indicating a location of the anatomical target based at least in part on the reconstructing.
|