| CPC G06Q 30/0631 (2013.01) [G06F 40/30 (2020.01); G06N 3/006 (2013.01); G06N 5/01 (2023.01); G06N 5/04 (2013.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G06Q 10/06315 (2013.01); G06Q 10/06316 (2013.01); G06Q 20/042 (2013.01); G06Q 20/24 (2013.01); G06Q 20/4016 (2013.01); G06Q 30/01 (2013.01); G06Q 30/018 (2013.01); G06Q 40/02 (2013.01); G06Q 40/03 (2023.01); G06Q 40/12 (2013.12); H04M 3/2218 (2013.01); H04M 3/5175 (2013.01); H04M 3/5191 (2013.01); H04W 12/08 (2013.01); G06Q 30/016 (2013.01); H04M 2203/403 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
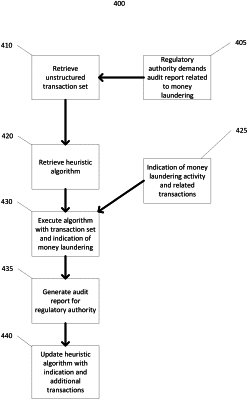
1. A computer-implemented method for predicting money laundering activity, comprising:
training, by one or more processors, a machine learning model based on a first transaction set, wherein:
the first transaction set is associated with a plurality of users and indicates at least one instance of first money laundering activity, and
the training identifies characteristics, indicated in the first transaction set, that are predictive of the at least one instance of the first money laundering activity;
receiving, by the one or more processors, a request identifying a particular financial account associated with at least one transaction;
retrieving, by the one or more processors, a second transaction set associated with the particular financial account based on the request; and
generating, by the one or more processors, using the machine learning model, and based on instances of one or more of the characteristics that are associated with the particular financial account and are indicated by the second transaction set, a prediction of second money laundering activity associated with the particular financial account and the at least one transaction.
|