| CPC G06Q 10/06315 (2013.01) [G06Q 10/04 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
1. A system of efficiently determining fair-share bands of a supply chain planning problem modeled as a multi-objective hierarchical linear programming problem, comprising:
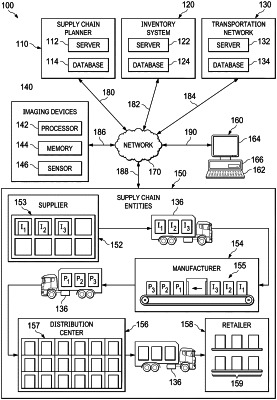
one or more imaging devices comprising one or more electronic devices configured to receive imaging information from one or more sensors, the one or more imaging devices configured to generate a mapping of one or more items to determine a current location of the one or more items at one or more supply chain entities;
a computer, comprising a processor and memory, the computer configured to:
receive supply chain input data for the supply chain planning problem;
receive product data from automated robotic machinery comprising at least one sensor, wherein the product data corresponds to an item of the one or more items detected by the automated robotic machinery;
model the supply chain planning problem as a multi-objective hierarchal linear programming problem having a first objective and at least one additional objective, and based, at least in part, on the supply chain input data;
assign weights at each band of a fixed number of at least two bands, wherein the weights follow a multi-variate Gaussian distribution, wherein an effective number of bands is a number of bands which have at least a minimum threshold gap between two consecutive bands;
determine a direction of improved band values from a value of a Key Process Indicator (KPI) calculated from an expected demand and short quantities, wherein the expected demand and short quantities are calculated from the multi-objective hierarchical linear programming problem using a sample generated by Gibbs sampling of a conditional Gaussian Bayesian Network, and further wherein the direction of improved band values is based, at least in part, on one or more unknown components and one or more observed components;
solve each of the first objective and the at least one additional objective of the multi-objective hierarchical linear programming problem;
generate a supply chain plan based, at least in part, on a solution of the supply chain planning problem after updating the objectives based, at least in part, on the improved band values;
generate a first mapping and a second mapping of an item, the first mapping associated with a first current location of the item, and the second mapping associated with a second past location of the item, wherein the first mapping and the second mapping are based on one or more detections by the automated robotic machinery;
compare the first mapping and the second mapping to determine if the first current location of the item is different from the second past location of the item;
monitor one or more supply chain constraints of the one or more items at the one or more supply chain entities and adjust a current inventory of the one or more supply chain entities by sending instructions to the automated robotic machinery according to the generated supply chain plan and based, at least in part, on the one or more supply chain constraints and one or more differences between the first mapping and the second mapping;
in response to sending the instructions to the automated robotic machinery, automatically locate items to add or remove from the current inventory of the one or more supply chain entities; and
automatically add or remove, by the automated robotic machinery, the automatically located items from the current inventory.
|