| CPC G06F 9/485 (2013.01) [G06F 8/75 (2013.01); G06F 9/5016 (2013.01)] | 22 Claims |
|
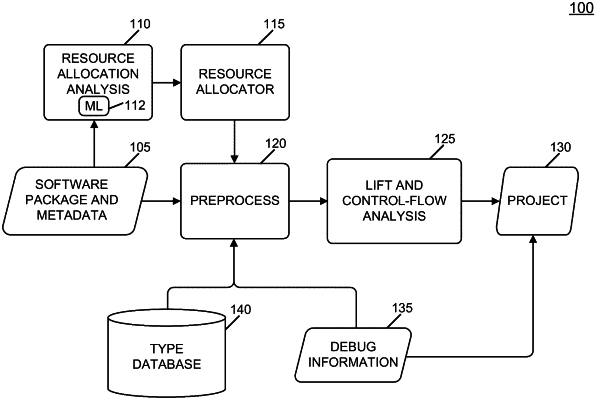
1. A method for implementation by one or more computing devices comprising:
receiving a software package for analysis;
extracting or deriving features from the software package;
determining, by inputting the features into a machine learning model, an estimated peak memory usage required to analyze the software package, the machine learning model being trained using a dataset generated by monitoring memory usage when analyzing a plurality of different software packages;
determining a number of memory resource units required for the determined peak memory usage;
queuing the software package in a backoff queue when a number of available memory resource units does not exceed the determined number of required memory resource units;
allocating the determined required memory resource units to analyze the software package when a number of available memory resource units equals or exceeds the determined number of required memory resource units; and
analyzing the software package using the allocated memory units.
|