| CPC G06F 16/24545 (2019.01) [G06F 16/24549 (2019.01); G06F 16/953 (2019.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
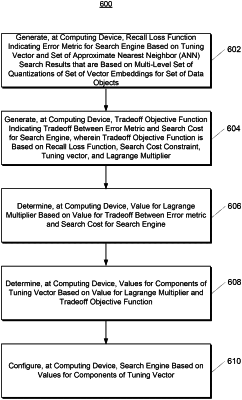
1. A computer-implemented method for operating a search engine, the method comprising:
generating, by a computing system comprising one or more computing devices, a recall loss function indicating an error metric for the search engine based on a tuning vector and a set of approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) search results that is based on a multi-level set of quantizations of a set of vector embeddings for a set of data objects;
generating, by the computing system, a tradeoff objective function indicating a tradeoff between the error metric and a search cost for the search engine, wherein the tradeoff objective function is based on the recall loss function, a search cost constraint, the tuning vector, and a Lagrange multiplier;
determining, by the computing system, a value for the Lagrange multiplier based on a value for the tradeoff between the error metric and the search cost for the search engine;
determining, by the computing system, values for components of the tuning vector based on the value for the Lagrange multiplier and the tradeoff objective function;
configuring, by the computing system, the search engine based on the values for the components of the tuning vector; and
processing, by the computing system, one or more search queries using the configured search engine in an online mode.
|