| CPC G01N 33/487 (2013.01) [G06N 3/04 (2013.01); G06T 7/0012 (2013.01); H04N 23/55 (2023.01); H04N 23/56 (2023.01); G06T 2207/20084 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30041 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
1. A system comprising:
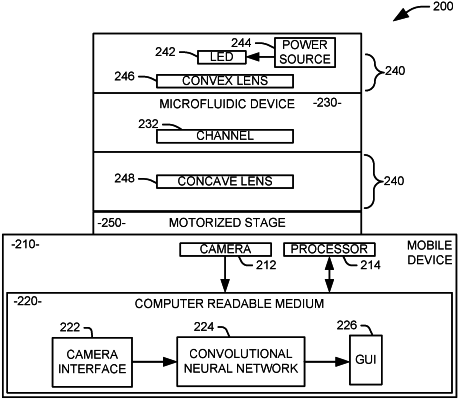
an optical assembly comprising at least one lens and having an associated axis;
a microfluidic device comprising a channel to hold a fluid sample from a subject and configured to engage with the housing such that the channel is aligned with the axis of the optical assembly;
a camera aligned with the axis of the optical assembly;
a processor; and
a non-transitory computer readable medium storing executable instructions for providing at least one image captured at the camera to a computer vision model to determine if there is a ferning pattern representative of a biological condition of the subject in the at least one image, the computer vision model being implemented as a convolutional neural network, comprising:
a plurality of convolutional layers, each applying a depth-wise convolution kernel to each of a plurality of channels within the network and a point-wise convolution that applies a one-by-one kernel across all of the plurality of channels within the network;
a fully connected layer that is connected to a last of the plurality of convolutional layers; and
a classification layer that is connected to the fully connected layer.
|