| CPC F03D 7/0284 (2013.01) [F03D 7/048 (2013.01); H02J 3/381 (2013.01); H02J 3/46 (2013.01); F05B 2270/1033 (2013.01); H02J 2300/28 (2020.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
1. A frequency support method for a wind farm, comprising:
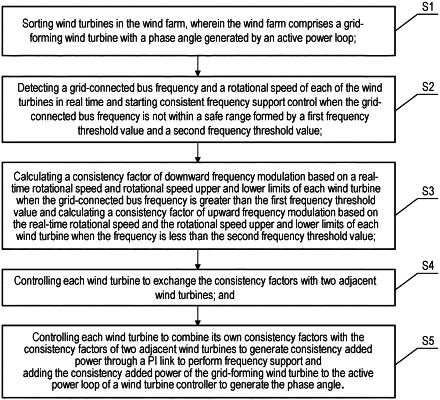
step 1: sorting wind turbines in the wind farm, wherein the wind farm comprises a grid-forming wind turbine with a phase angle generated by an active power loop, wherein the step 1 further comprises:
step 11: selecting a wind turbine and numbering the wind turbine as 1, testing communication time between wind turbine No. 1 and the remaining wind turbines, and numbering the wind turbine with the shortest communication time as wind turbine No. 2; and
step 12: testing the communication time between wind turbine No. 2 and the remaining unnumbered wind turbines and numbering the wind turbine with the shortest communication time as wind turbine No. 3 and so on to complete the numbering of all wind turbines in the wind farm;
step 2: detecting a grid-connected bus frequency and a rotational speed of each of the wind turbines in real time and starting consistent frequency support control when the grid-connected bus frequency is not within a safe range formed by a first frequency threshold value and a second frequency threshold value, wherein the consistent frequency support control is further defined in step 3;
step 3: calculating a consistency factor of downward frequency modulation based on a real-time rotational speed and rotational speed upper and lower limits of each wind turbine when the grid-connected bus frequency is greater than the first frequency threshold value, and calculating a consistency factor of upward frequency modulation based on the real-time rotational speed and the rotational speed upper and lower limits of each wind turbine when the frequency is less than the second frequency threshold value;
step 4: controlling each wind turbine to exchange the consistency factors with two adjacent wind turbines; and
step 5: controlling each wind turbine to combine its own consistency factors with the consistency factors of two adjacent wind turbines to generate consistency added power through a PI link to perform frequency support and adding the consistency added power of the grid-forming wind turbine to the active power loop of a wind turbine controller to generate the phase angle.
|