|
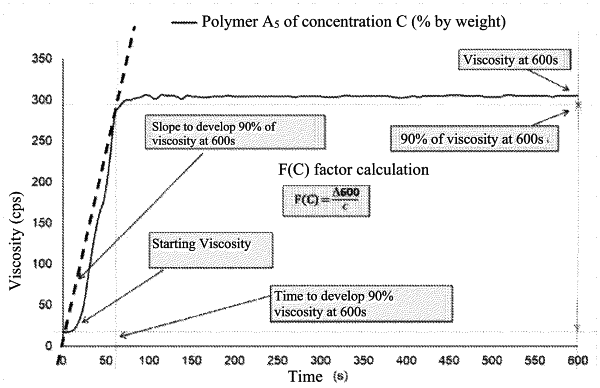
1. A method for making a paper or cardboard sheet, comprising, during a papermaking or cardboard sheet making process, adding a water-soluble polymer P of weight average molecular weight greater than 750,000 Daltons to a fiber suspension, wherein the method comprises the following successive steps: —preparing an aqueous solution A containing at least one water-soluble polymer P at a concentration C comprising between 0.1 and 0.5% by weight, said polymer P having a factor F(c) greater than 4, with F(c)=A600/C, A600 being the slope to reach 90% of the viscosity developed by aqueous solution A at 600 seconds at 25° C., obtained from the viscosity curve of aqueous solution A as a function of time, at the given concentration C, at 25° C., polymer P being, prior to the formation of aqueous solution A, in the form of an anhydrous oily suspension containing between 0.05 and 5.0% by weight of a rheology modifier and between 20 and 60% by weight of polymer P in the form of particles with a mean diameter of less than 300 μm, the viscosity of solution A over time being determined at 25° C. with the aid of a viscometer equipped with a helical geometry, —adding aqueous solution A to the fibrous suspension, and —forming a sheet of paper or cardboard using the fibrous suspension after aqueous solution A has been added thereto.
|