| CPC C10G 1/10 (2013.01) [C10B 49/22 (2013.01); C10B 53/07 (2013.01); C10B 57/06 (2013.01); C10G 2300/1003 (2013.01); C10G 2400/20 (2013.01); C10G 2400/22 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
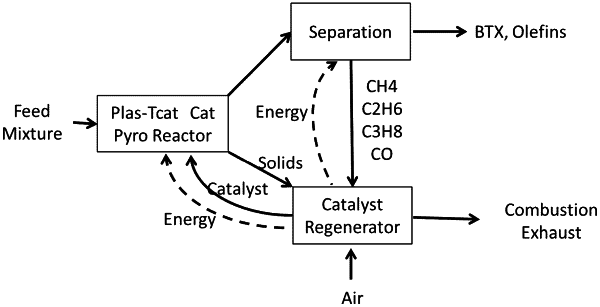
1. A method of catalytically pyrolyzing a mixed feed of materials, comprising:
providing a first stream comprising a polymer;
adding a high coke-forming material to form a mixed feed of materials;
adding the mixed feed of materials to a fluidized bed reactor;
pyrolyzing the mixed feed in the presence of a solid catalyst in the fluidized bed reactor to produce a fluid product stream and used catalyst with coke, and wherein at least 95% of the carbon in the mixed feed is converted to coke and volatile products;
transferring at least a portion of the used catalyst with coke to a regenerator where the coke is reacted with oxygen to form hot regenerated catalyst and returning at least a portion of the hot regenerated catalyst to the fluidized bed reactor wherein heat from the hot regenerated catalyst provides energy to the step of pyrolyzing; and wherein either
(a) heat from combusting the coke provides at least 90% of the energy to the step of pyrolyzing, wherein the first stream has the property such that if a stream consisting of only the first stream would be subjected to the step of pyrolyzing and if all of the used catalyst with coke would be transferred to the regenerator where the coke is combusted with oxygen to form the hot regenerated catalyst and hot combustion gases and returning all of the hot regenerated catalyst to the fluidized bed reactor wherein the heat from the hot regenerated catalyst provides energy to the step of pyrolyzing, then the heat provided by the combustion of the coke, including heat of the catalyst and heat recovered from the combustion gases, provides energy that would be less than the minimum energy required for the catalytic pyrolysis process in which at least 95% of the carbon in the first stream is converted to coke and volatile products; and
wherein the addition of the coke-forming materials to the mixed feed results in sufficient coke to provide, upon combustion of the coke, at least the minimum energy required for a catalytic pyrolysis process in which at least 95% of the carbon in the mixed feed is converted to coke and volatile products; or
(b) heat from combusting the coke and a portion of the volatile products provides at least 90% of the energy to the step of pyrolyzing,
wherein the first stream has the property such that if a stream consisting of only the first stream would be subjected to the step of pyrolyzing and if all of the used catalyst with coke and the portion of the volatile products would be transferred to the regenerator where the coke and the portion of the volatile products is combusted with oxygen to form the hot regenerated catalyst and hot combustion gases and returning all of the hot regenerated catalyst to the fluidized bed reactor wherein the heat from the hot regenerated catalyst provides energy to the step of pyrolyzing, then the heat provided by the combustion of the coke, including heat of the catalyst and heat recovered from the combustion gases, provides energy that would be less than the minimum energy required for the catalytic pyrolysis process in which at least 95% of the carbon in the first stream is converted to coke and volatile products; and
wherein the addition of the coke-forming materials to the mixed feed results in sufficient coke and a portion of volatile products to provide, upon combustion of the coke and portion of volatile products, at least the minimum energy required for a catalytic pyrolysis process in which at least 95% of the carbon in the mixed feed is converted to coke and volatile products.
|