| CPC C07H 1/00 (2013.01) [C07F 7/1804 (2013.01); C07H 15/10 (2013.01); C07H 15/18 (2013.01); C07H 15/203 (2013.01)] | 22 Claims |
|
1. A method comprising admixing at least one fluoroglycoside of formula (I) and a silyl ether glycoside, in the presence of a catalyst having a formula B (Ar1)(Ar2)(Ar3) under conditions sufficient to form a glycoside product:
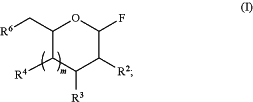 wherein
each of R2, R3, R4, and R6 is independently H, C1-6 alkyl, —N(R1)2, —N3, CO2H, CO2C1-6alkyl, or —ORPG, or
two of R2, R3, R4, and R6, together with the atoms to which they are attached form a five to eight membered heterocycloalkyl having 1 to 3 ring heteroatoms selected from O, N, and S;
each of Ar1, Ar2, Ar3 is independently a halophenyl;
each R1 is independently H, C(O)C1-6alkyl, or an amino protecting group;
m is 0 or 1; and
each RPG is independently a hydroxyl protecting group or a saccharide.
|