| CPC C07D 413/14 (2013.01) [C07D 413/04 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
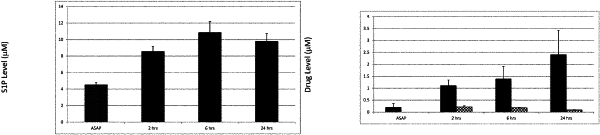
|
1. A method of treating a disease in a patient suffering therefrom, wherein the disease is selected from a neoplastic disease, a disease involving excess vascular growth, an allergic disease, an inflammatory disease of the eye, an inflammatory disease of the kidney, a fibrotic disease, an autoimmune disease, acute lung injury, sepsis, capillary leak syndrome, pneumonia, ischemia reperfusion injury, acute kidney injury, age-related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, atherosclerosis, and pulmonary arterial hypertension,
the method comprising administering to the patient an effective amount of a compound according to formula (I)
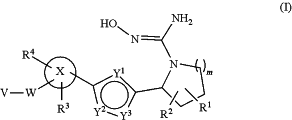 wherein
X is phenyl;
R1 and R2 are independently selected from the group consisting of H, OH, —(C1-C6)alkyl-OH, halo, NH2, NOH, NHOH, and CN;
or R1 and R2, if bound to adjacent carbon atoms, in combination with the existing carbon-carbon bond represent a double bond between the adjacent carbon atoms;
R3 and R4 are independently selected from the group consisting of H, (C1-C6)alkyl, (C3-C8)cycloalkyl, (C1-C6)haloalkyl, CN, and halo;
wherein one of R3 and R4 is —CF3;
m=1;
W is CH2 or O;
V is selected from the group consisting of (C1-C10)alkyl, (C2-C12)alkenyl, —(C1-C10)alkyl-(C6-C10)aryl, —(C2-C12)alkenyl-(C6-C10)aryl, —(C1-C10)alkyl-(C6-C10)aryl-(C1-C10)alkyl, —(C1-C10)alkyl-(C3-C8)cycloalkyl, —(C1-C10)alkyl-heterocyclyl containing from 1 to 3 ring heteroatoms selected from N, O, and S;
wherein any aryl is optionally fused to (C6-C10)aryl, (C3-C8)cycloalkyl, or heterocyclyl containing from 1 to 3 ring heteroatoms selected from N, O, and S
wherein any alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, or aryl is optionally substituted by 1-4 substituents independently selected from the group consisting of F, Cl, Br, (C1-C6)alkyl, —O—(C1-C6)alkyl, (C2-C6)alkenyl, (C1-C6)haloalkyl, (C6-C10)aryl, and CN;
Y1 is N;
Y2 is N and Y3 is O, or Y2 is O and Y3 is N;
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
|