| CPC B60W 60/0018 (2020.02) [B60W 60/0016 (2020.02); B60W 2420/403 (2013.01); B60W 2420/408 (2024.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
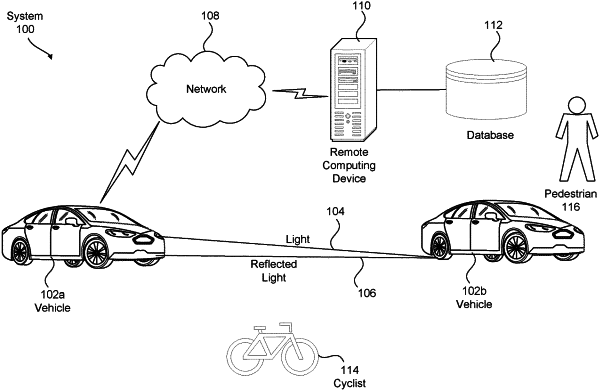
1. A method, comprising:
detecting, by an asymmetrical Autonomous Vehicle System (AVS), that a failure of one or more AVS components has occurred for a vehicle;
determining, by the asymmetrical AVS, a level of criticality of the failure based on a severity of the failure and a minimal risk condition (MRC) for selected driving tasks of a vehicle mission;
determining, by the asymmetrical AVS, a subset of AVS backup components to complete the vehicle mission at the level of criticality;
activating, by the asymmetrical AVS, the AVS backup components necessary to complete the vehicle mission at the level of criticality, wherein the backup AVS components comprise one or more sensors and one or more vehicle controllers;
processing, by the asymmetrical AVS, data points received from the one or more sensors to determine an input to the one or more vehicle controllers; and
controlling, by the asymmetrical AVS and the vehicle controllers, the vehicle to complete the mission at the level of criticality.
|