| CPC B01D 61/465 (2022.08) [B01D 61/445 (2013.01); B01D 61/466 (2022.08); B01D 69/02 (2013.01); B01D 69/12 (2013.01); B01J 43/00 (2013.01); B01J 45/00 (2013.01); B01J 47/12 (2013.01); C02F 1/42 (2013.01)] | 6 Claims |
|
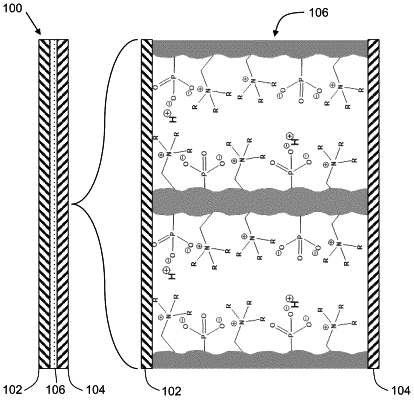
1. A bipolar membrane (BPM) (100) for enhancing a rate of water dissociation or formation, said BPM (100) comprising a cation-exchange membrane (CEM) layer (102), an anion-exchange membrane (AEM) layer (104), and a catalytic polymer layer (106) interfacing and juxtaposed between the CEM layer (102) and the AEM layer (104),
wherein the catalytic polymer layer (106) comprises a polymer backbone functionalized with catalytic buffer groups, the catalytic buffer groups comprising proton-transfer functional groups, proton-transfer coordination compounds, or combinations thereof, wherein the proton-transfer catalytic functional groups have a pka in the range of about 6 to 8 and the proton-transfer catalytic coordination compounds have a pKf in the range of about 4 to 10,
wherein the proton-transfer functional groups comprise amines, pyrazines pyrimidines, pyridazines, imidazoles, piperazines, morpholines, boronates, phosphonates, nucleobases, or amino acids, and
wherein the proton-transfer coordination compounds comprise ligated cationic zinc, copper, iron, or lead.
|