| CPC A61K 9/1641 (2013.01) [A61K 9/5192 (2013.01); A61K 31/506 (2013.01); A61K 47/6935 (2017.08); A61K 47/6937 (2017.08); A61P 35/00 (2018.01)] | 19 Claims |
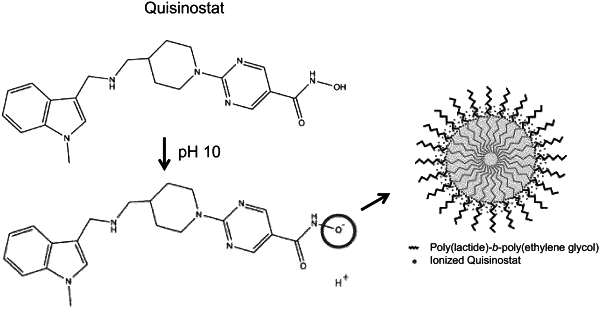
|
1. A method of fabricating a therapeutic nanoparticle, comprising:
a. preparing an aqueous phase;
b. adjusting a pH of the aqueous phase to a basic pH;
c. mixing an organic phase with the aqueous phase, wherein the organic phase comprises an organic solvent and a nanoparticle comprising an amphiphilic polymer, wherein the amphiphilic polymer is selected from the group consisting of poly(lactic acid)-poly(ethylene glycol) (PLA-PEG), poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-poly(ethylene glycol), poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-d-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol succinate, poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-ethylene oxide fumarate, poly(glycolic acid)-poly(ethylene glycol), polycaprolactone-poly(ethylene glycol), and a combination thereof;
d. partially removing the organic solvent to drive nanoparticle formation;
e. after step (d), adding a water-insoluble biologically active ingredient, wherein the active ingredient is a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor comprising a weak acid ionizable group, and wherein the basic pH of the aqueous phase ionizes the weak acid ionizable group; and
f. removing the remaining organic solvent via evaporation;
wherein water solubility of the active ingredient increases in pH 10 or above and the load of the active ingredient in the nanoparticle comprising the amphiphilic polymer also increases in the pH 10 or above.
|