| CPC A61B 17/32002 (2013.01) [A61B 17/142 (2016.11); A61B 17/1633 (2013.01); A61B 17/1671 (2013.01); A61B 2017/0046 (2013.01); A61B 17/15 (2013.01); A61B 17/1617 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
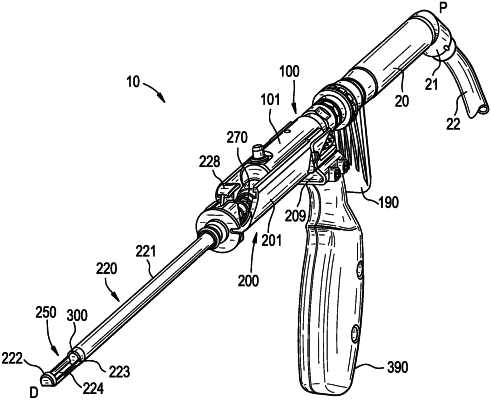
1. A bone and tissue resection device, comprising:
a stationary assembly including:
a housing configured to couple an elongated sleeve extending distally from the housing, the elongated sleeve having a distal cutting region,
a handle coupled to the housing, and
a depth adjustment mechanism; and
a drive assembly including:
a housing slidably coupled to the housing of the stationary assembly to permit selective proximal and distal translation of the drive assembly relative to the stationary assembly by the depth adjustment mechanism, and
a drive mechanism disposed within the drive assembly housing and configured to:
couple with a blade shaft extending through the elongated sleeve such that the selective proximal and distal translation of the drive assembly relative to the stationary assembly causes a corresponding proximal or distal translation of the blade shaft in the elongated sleeve, and
engage with a source of continuous rotational motion and convert the continuous rotational motion into oscillating rotational motion of the blade shaft, when coupled.
|