| CPC H05K 7/20927 (2013.01) [G01F 1/69 (2013.01); H05K 7/20945 (2013.01)] | 9 Claims |
|
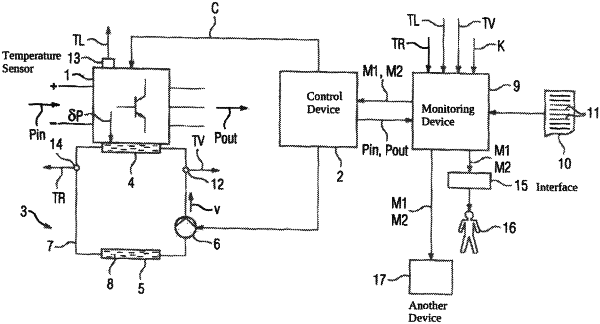
1. A method for monitoring a coolant circuit, the method comprising:
cooling a conversion device giving rise to a power loss with a coolant flowing in the coolant circuit;
sending to a monitoring device as a measurement value an inflow temperature at which the coolant is supplied to the conversion device;
determining with the monitoring device a flow velocity at which the coolant flows in the coolant circuit based on operating data of the conversion device and/or the coolant circuit, a quantity of heat to be removed per unit of time by the coolant known to the monitoring device, a local temperature of the conversion device known to the monitoring device, and the inflow temperature;
comparing with the monitoring device the determined flow velocity with a limit velocity;
resorting with the monitoring device to a special reaction when the determined flow velocity reaches or exceeds the limit velocity; and
resorting with the monitoring device to either no reaction at all or to a normal reaction that is not the same as the special reaction as long as the determined flow velocity does not reach the limit velocity.
|