| CPC H02N 2/181 (2013.01) [H10N 30/30 (2023.02)] | 2 Claims |
|
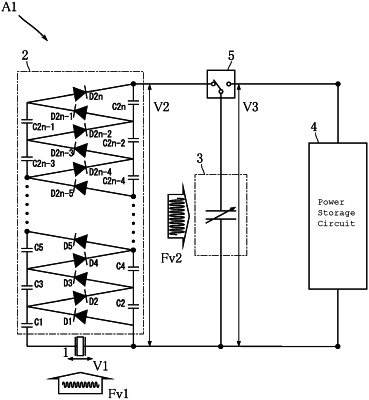
1. A dielectric elastomer power generation system comprising:
a dielectric elastomer power generation element including a dielectric elastomer layer and a pair of electrodes sandwiching the dielectric elastomer layer;
a piezoelectric element;
a multi-stage voltage multiplier/rectifier circuit that boosts and rectifies a voltage generated by the piezoelectric element and applies a resulting voltage to the dielectric elastomer power generation element as initial charge;
a power storage circuit that receives electric power generated by the dielectric elastomer power generation element, and
a switching unit that can perform control of an electrical connection between the dielectric elastomer power generation element and the multi-stage voltage multiplier/rectifier circuit, and an electrical connection between the dielectric elastomer power generation element and the power storage circuit based on a vibration state of the piezoelectric element or a stretched or contracted state of the dielectric elastomer power generation element.
|