| CPC G06T 5/009 (2013.01) [G06T 5/40 (2013.01); G06T 5/50 (2013.01); G06T 7/0002 (2013.01); H04N 5/20 (2013.01); G06T 2200/24 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10016 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20208 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
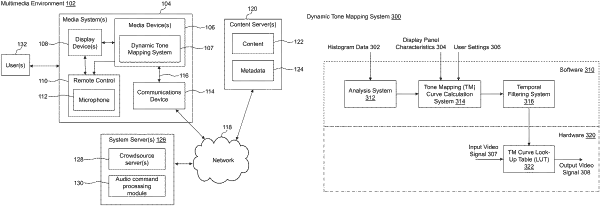
1. A computer-implemented method for dynamic tone mapping of video content, comprising:
receiving, by a dynamic tone mapping system executing on a media device, histogram data associated with a first video signal representing a video program, wherein the first video signal has a first dynamic range and static metadata describing one or more brightness characteristics of the video program, wherein the histogram data comprises color values for a plurality of frames in the first video signal outputted by a display device;
determining, by the dynamic tone mapping system, a cumulative histogram for a scene in the video program based on the histogram data;
determining, by the dynamic tone mapping system, a near-brightest pixel for the scene in the video program based on the cumulative histogram, wherein the near-brightest pixel is a representative pixel value that defines a maximum target brightness value for proper display of the scene;
modifying, by the dynamic tone mapping system, a tone mapping curve based on the near-brightest pixel and characteristics of the display device to generate a modified tone mapping curve; and
converting, by the dynamic tone mapping system, the first video signal based on the modified tone mapping curve to generate a second video signal having a second dynamic range that is less than the first dynamic range.
|