| CPC G06Q 40/04 (2013.01) [G06Q 40/06 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
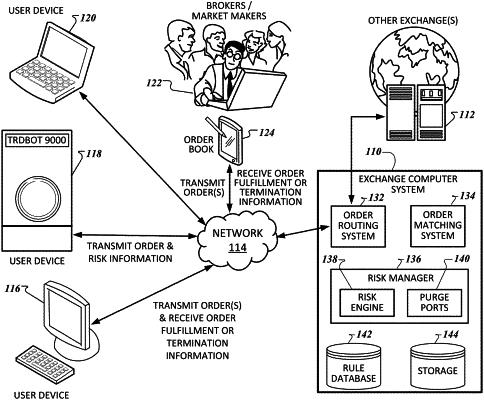
1. A method for risk implemented control via an exchange computer system, the method comprising:
receiving, by the exchange computer system from an electronic device remote to the exchange computer system and through a computer network, data indicative of one or more parameters for configuring a risk profile, wherein the computer network comprises a network of interconnected electronic devices, wherein the exchange computer system comprises a risk engine processor, one or more purge ports, and a database, and is configured to receive orders from a second exchange computer system different from the exchange computer system;
generating, by the risk engine processor, the risk profile based on the data indicative of the one or more parameters;
storing the risk profile that is received from the risk engine processor in the database;
monitoring, by the risk engine processor, market data indicative of market conditions;
determining, based on the monitoring of the market data, that a notional value of one or more security transaction orders indicated by the market data satisfies a risk threshold, wherein the risk threshold includes a gross notional limit or a net notional limit, and the market data indicates whether the gross or net notional limit is satisfied;
receiving, at the one or more purge ports, instructions from a risk manager, the risk manager comprising the risk engine processor and the one or more purge ports;
configuring the one or more purge ports such that each of the one or more purge ports is limited to a particular number and type of risk profiles;
assigning, by the risk engine processor, the risk profile to a set of the one or more purge ports; and
canceling, by the risk engine processor, in response to determining that the risk threshold is satisfied upon receiving instruction at one of the one or more purge ports from the risk engine processors, the one or more security transaction orders associated with the risk profile having the gross notional limit or the net notional limit.
|