| CPC G06F 16/787 (2019.01) [G06F 16/75 (2019.01); G06F 16/9024 (2019.01); G06F 40/56 (2020.01); G06N 3/08 (2013.01); G06V 20/47 (2022.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
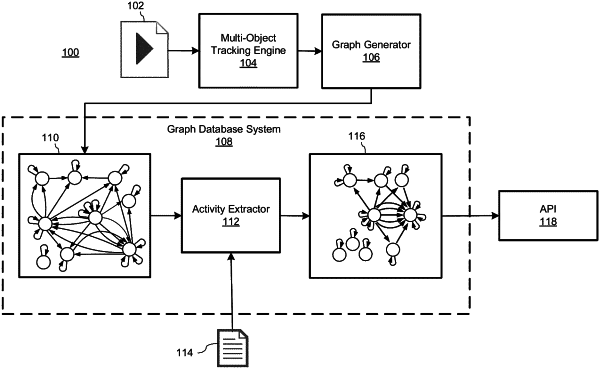
1. A method comprising:
receiving a scene including a plurality of tracks, each track of the plurality of tracks corresponding to an entity and each track of the plurality of tracks being associated with a bounding box;
determining, based on a distance between a plurality of the bounding boxes, a defined spatial proximity between the plurality of the bounding boxes;
building a spatiotemporal proximity graph based on the plurality of tracks; and
identifying, based on the spatiotemporal proximity graph and the spatial proximity, a spatiotemporal relationship between a plurality of the entities.
|