| CPC G03F 7/0392 (2013.01) [G03F 7/0042 (2013.01); G03F 7/0043 (2013.01); G03F 7/2004 (2013.01)] | 9 Claims |
|
1. A process of forming a polymer resist, comprising:
providing an alternating copolymer having repeat units each comprising an ultraviolet (EUV)-absorbing element A; and
reacting end groups of the alternating copolymer with monofunctional monomers selected from the group consisting of trimethyltin hydride, triethyltin hydride, tripropyltin hydride, tributyltin hydride, triphenyltin hydride, trimethyltin diethylamide, triethyltin diethylamide, tripropyltin diethylamide, tri-n-butyltin diethylamide, tri-t-butyltin diethylamide, trimethyltellurium iodide, tetraphenylantimony bromide, tetra-m-tolylbismuth iodide, and tetramethylbismuth chloride to form a polymer having the following structure:
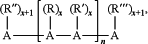 wherein:
n is an integer greater than 1
x=2 or 3; and
R, R′, R″, and R′″ are each hydrocarbon ligands.
|