| CPC A61M 5/1723 (2013.01) [A61M 2205/52 (2013.01); A61M 2230/201 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
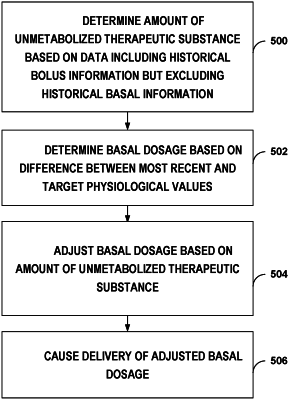
1. A processor-implemented method for closed-loop control in steady-state conditions, the method comprising:
determining, based on data including historical bolus information but excluding historical basal information, an amount of unmetabolized therapeutic substance in a patient;
determining, based on a difference between a most recent measurement of a physiological condition of the patient and a target value for the physiological condition, a first amount or rate of a basal dosage for delivery to the patient;
adjusting, based on the amount of unmetabolized therapeutic substance, the first amount or rate of the basal dosage to determine a second amount or rate of the basal dosage; and
causing delivery of the second amount or rate of the basal dosage based on communicating the second amount or rate in a delivery command.
|
|
8. A system for closed-loop control in steady-state conditions, the system comprising:
one or more processors; and
one or more processor-readable storage media storing instructions which, when executed by the one or more processors, cause performance of:
determining, based on data including historical bolus information but excluding historical basal information, an amount of unmetabolized therapeutic substance in a patient;
determining, based on a difference between a most recent measurement of a physiological condition of the patient and a target value for the physiological condition, a first amount or rate of a basal dosage for delivery to the patient;
adjusting, based on the amount of unmetabolized therapeutic substance, the first amount or rate of the basal dosage to determine a second amount or rate of the basal dosage; and
causing delivery of the second amount or rate of the basal dosage based on communicating the second amount or rate in a delivery command.
|
|
15. One or more non-transitory processor-readable storage media storing instructions which, when executed by one or more processors, cause performance of:
determining, based on data including historical bolus information but excluding historical basal information, an amount of unmetabolized therapeutic substance in a patient;
determining, based on a difference between a most recent measurement of a physiological condition of the patient and a target value for the physiological condition, a first amount or rate of a basal dosage for delivery to the patient;
adjusting, based on the amount of unmetabolized therapeutic substance, the first amount or rate of the basal dosage to determine a second amount or rate of the basal dosage; and
causing delivery of the second amount or rate of the basal dosage based on communicating the second amount or rate in a delivery command.
|