| CPC A61B 5/14865 (2013.01) [A61B 5/1459 (2013.01); A61B 5/14532 (2013.01); G01N 27/30 (2013.01); G01N 27/419 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. A method comprising:
providing a sensor to detect a molecule of interest, the sensor comprising:
a substrate;
a working electrode on the substrate;
a reference electrode on the substrate;
a counter electrode on the substrate; and
an enzyme layer covering the working electrode, and implanting the sensor in biological tissue;
applying a plurality of voltages to the working electrode;
measuring a plurality of currents at the working electrode, each current of the plurality of currents corresponding to a voltage of the plurality of voltages, the plurality of currents comprising a first current and a second current, the first current being higher than the second current;
generating a measurement curve of the plurality of currents plotted against the plurality of voltages;
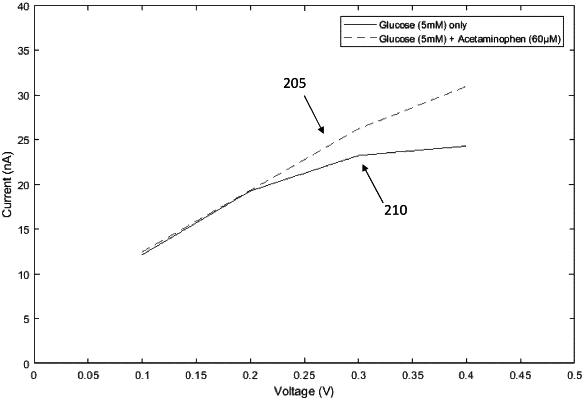
comparing the measurement curve to a reference curve, the reference curve corresponding to a measurement of the molecule of interest without interfering species, the reference curve consisting of a graph of positive currents versus positive voltages; and,
if the measurement curve corresponds to the reference curve:
selecting the first current of the plurality of currents corresponding to a first voltage; and
calculating a concentration of the molecule of interest based on the first current but not the second current;
if the measurement curve does not correspond to the reference curve:
selecting the second current of the plurality of currents corresponding to a second voltage, the second voltage being lower than the first voltage; and
calculating a concentration of the molecule of interest based on the second current but not the first current.
|