| CPC A61B 34/73 (2016.02) [A61B 17/221 (2013.01); A61K 9/0034 (2013.01); A61K 9/14 (2013.01); A61B 2017/0034 (2013.01); A61B 2017/00876 (2013.01); A61B 2017/22082 (2013.01); A61B 2034/731 (2016.02)] | 10 Claims |
|
1. A medical device for retrieval of kidney stone fragments from a urinary tract, comprising:
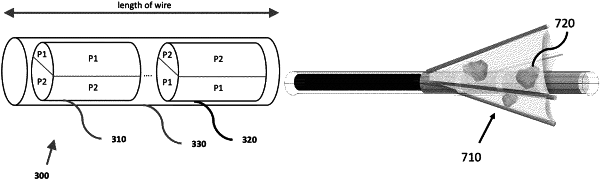
a plurality of magnets arranged within a flexible sheath forming a flexible wire,
wherein the magnets are magnetically attached end-to-end and arranged with their magnetic polarities alternating in direction;
wherein the magnetization direction of each of the magnets is orthogonal to the length axis of the flexible wire;
wherein there is a removable inner stylet within the flexible sheath allowing for modifiable flexibility of the wire;
wherein the medical device is dimensioned to be introduced into the urinary tract and standard endoscopic devices;
wherein the medical device is dimensioned to allow for the wire with magnetically attached stone fragments to be retrieved from the urinary tract;
wherein the magnetic field along the length axis is sufficient to attract to the surface of the flexible wire superparamagnetic nanoparticles which have bound themselves to kidney stone fragments; and
wherein the kidney stone fragments comprise calcium, uric acid, struvite, cystine or a combination thereof.
|