| CPC A01N 1/0247 (2013.01) | 20 Claims |
|
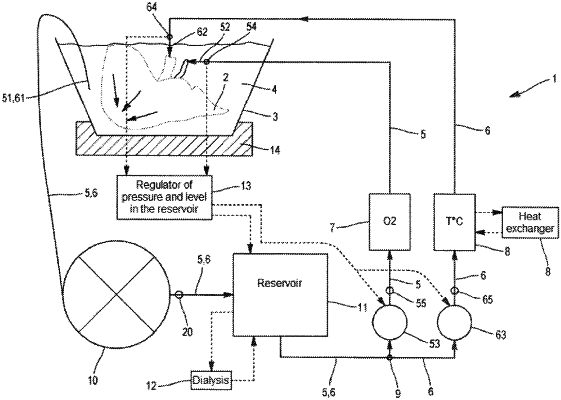
1. An organ perfusion device, comprising:
a fluid container configured to hold an organ submerged in a perfusion fluid having a concentration of oxygen dissolved therein;
a first fluid channel comprising a first inlet configured to be submerged in the container, a first outlet configured to be submerged in the container, and a first pump configured to circulate the perfusion fluid from the first inlet to the first outlet;
a second fluid channel comprising a second inlet configured to be submerged in the container, a second outlet configured to be submerged in the container, and a second pump configured to circulate the perfusion fluid from the second inlet to the second outlet; and
an oxygenation means configured to increase the concentration of oxygen dissolved in the perfusion fluid;
wherein the concentration of oxygen dissolved in the perfusion fluid leaving the first outlet is greater than the concentration of oxygen dissolved in the perfusion fluid leaving the second outlet.
|